Dec 19, 2009 Support Communities / Mac OS & System Software / Mac OS X v10.4 Tiger Search or ask a question Search Apple Communities Reset. I was trying to install a software from the terminal. The software does not have a.dmg version. So I have to use 'make install'. I was denied because of the permission issue.
These advanced steps are primarily for system administrators and others who are familiar with the command line. You don't need a bootable installer to upgrade macOS or reinstall macOS, but it can be useful when you want to install on multiple computers without downloading the installer each time.
Download macOS
Find the appropriate download link in the upgrade instructions for each macOS version:
macOS Catalina, macOS Mojave, ormacOS High Sierra
Installers for each of these macOS versions download directly to your Applications folder as an app named Install macOS Catalina, Install macOS Mojave, or Install macOS High Sierra. If the installer opens after downloading, quit it without continuing installation. Important: To get the correct installer, download from a Mac that is using macOS Sierra 10.12.5 or later, or El Capitan 10.11.6. Enterprise administrators, please download from Apple, not a locally hosted software-update server.
OS X El Capitan
El Capitan downloads as a disk image. On a Mac that is compatible with El Capitan, open the disk image and run the installer within, named InstallMacOSX.pkg. It installs an app named Install OS X El Capitan into your Applications folder. You will create the bootable installer from this app, not from the disk image or .pkg installer.
Use the 'createinstallmedia' command in Terminal
- Connect the USB flash drive or other volume that you're using for the bootable installer. Make sure that it has at least 12GB of available storage and is formatted as Mac OS Extended.
- Open Terminal, which is in the Utilities folder of your Applications folder.
- Type or paste one of the following commands in Terminal. These assume that the installer is still in your Applications folder, and MyVolume is the name of the USB flash drive or other volume you're using. If it has a different name, replace
MyVolumein these commands with the name of your volume.
Catalina:*
Mojave:*
High Sierra:*
El Capitan: - Press Return after typing the command.
- When prompted, type your administrator password and press Return again. Terminal doesn't show any characters as you type your password.
- When prompted, type
Yto confirm that you want to erase the volume, then press Return. Terminal shows the progress as the bootable installer is created. - When Terminal says that it's done, the volume will have the same name as the installer you downloaded, such as Install macOS Catalina. You can now quit Terminal and eject the volume.
* If your Mac is using macOS Sierra or earlier, include the --applicationpath argument, similar to the way this argument is used in the command for El Capitan.
Use the bootable installer
After creating the bootable installer, follow these steps to use it:
- Plug the bootable installer into a compatible Mac.
- Use Startup Manager or Startup Disk preferences to select the bootable installer as the startup disk, then start up from it. Your Mac will start up to macOS Recovery.
Learn about selecting a startup disk, including what to do if your Mac doesn't start up from it. - Choose your language, if prompted.
- A bootable installer doesn't download macOS from the Internet, but it does require the Internet to get information specific to your Mac model, such as firmware updates. If you need to connect to a Wi-Fi network, use the Wi-Fi menu in the menu bar.
- Select Install macOS (or Install OS X) from the Utilities window, then click Continue and follow the onscreen instructions.
Learn more
For more information about the createinstallmedia command and the arguments that you can use with it, make sure that the macOS installer is in your Applications folder, then enter this path in Terminal:
Catalina:
Mojave:
High Sierra:
El Capitan:
After you’ve configure a new Mac from scratch or reloaded macOS, installing a dozen or more apps is an overwhelming job. Visiting all the right websites and setting the apps up according to your needs is a hassle.
You can solve this problem with a package manager. Homebrew is a package manager for macOS that simplifies the installation of free Unix tools and GUI apps. We’ll show you how to install apps with Homebrew and keep them up-to-date without any trouble.
What Is Homebrew?
Homebrew a free and open source package manager that lets you easily install command line tools The Mac Terminal Commands Cheat SheetOur mega cheat sheet of Mac terminal commands provides a great reference for all the important commands you should know. Read More and GUI apps on macOS. With a single command, you can search, install, uninstall, or update free Unix tools. Before installing Homebrew, you’ll need the following:
- Terminal, located in the /Application/Utilities folder.
- macOS 10.12 (Sierra) or higher.
- Command Line Tools, or Xcode from the Mac App Store.
How to Install Homebrew on Mac
If you have Xcode installed, there’s no need to install Command Line Tools, since the package is already baked into Xcode. But if not, you don’t have to install Xcode just for Homebrew.
After installation, Xcode consumes around 10GB of disk space, which is no small amount. If you’re just getting started with these commands, then installing Command Line Tools (roughly 150MB) will get the job done.
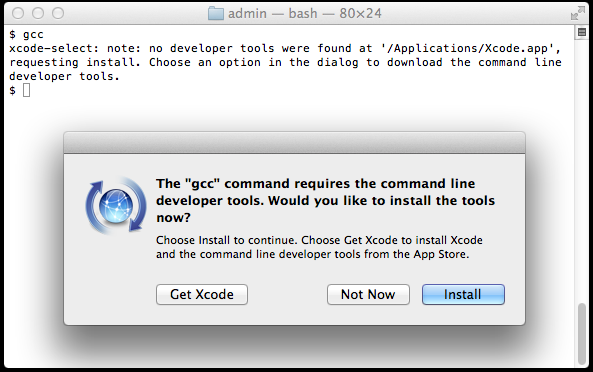
Step 1: Install Command Line Tools
To install Command Line Tools, press Cmd + Space to launch Spotlight and search for Terminal. Then type:
As you type this command, a popup will appear with the message The “xcode-select” command requires the command line developer tools. Would you like to install these tools now? Click the Install button to proceed with the installation.
In my case, since the package is already installed, this shows an error message.
Step 2: Install Homebrew
To install Homebrew, copy and paste the following command into the Terminal:
Install Mac Software On Windows
When you paste this command, you’ll see a series of lines about what the script will install and where. Press Return again to continue, or any other key to cancel.
Then enter the administrator password to begin the installation. Installation takes a bit of time, depending on the speed of your Mac and internet connection. On completion, you’ll see an Installation successful message.
Step 3: Verify the Homebrew Installation
Run this command to validate the Homebrew installation and check for any errors:
If you see any Warnings messages, you can safely ignore them, but you should check out common issues that might affect a Homebrew installation. In most cases, you won’t see any errors if your copy of macOS and Command Line Tools/Xcode are up to date.
You should this check for any pending updates in the App Store before you install Homebrew.
Installing Popular Unix Tools With Homebrew
Since Homebrew is a package manager, it automates the entire process of installing, updating, and removing apps from the system. It compiles packages and handles all the dependencies for you.
For example, one app might rely on two others to work properly. Rather than installing those other apps yourself, Homebrew installs them and configures them to work with your requested app without any issues.
Here are a few handy tools you can install with Homebrew:
- youtube-dl: Lets you download videos from YouTube and other more sites.
- geoip: Gives you the geolocation data for a particular IP address. Useful for system administrators, security researchers, and web developers.
- wget: Lets you download data from the web and FTP. You can download a file or even an entire website with this tool.
- cask: This one lets you install macOS apps with a GUI.
- htop: Command line alternative of Activity Monitor. It gives you thorough information on CPU, memory, processes, and more.
Manage Unix Tools With Homebrew
Running these Homebrew formulas is easy. Just type:
To install youtube-dl, for instance, type in:
Type the following to see the list of commands that Homebrew supports:
You can browse a big list of available commands on the Homebrew formulae page. And use the following commands for more options:
- search: Search for a formula
- uninstall: Uninstall a formula
- list: List all the installed formulas
- upgrade: Fetch the newest version of Homebrew from Github
- upgrade [formula name]: Install updates for a particular formula
How to Install Homebrew Cask on Mac
Homebrew Cask extends Homebrew and lets you easily install macOS GUI apps directly from the command line. With this simple script, you can install and manage many apps without needing to download them individually and go through the typical drag-and-drop routine.
To install Cask, type this into Terminal:
Just after installing Cask, type this:
The second Cask command is intended for installing alternate versions of Casks. For example, they include betas, development versions of browsers you might want to install, latest versions of legacy open source apps, and more.
With Cask installed, you can also enter this command:
This syntax will tell you commands that Cask supports. Every time you use a command, don’t forget to prepend with brew cask. The most frequently used commands you need to remember are:
- install: Installs the given cask
- uninstall: Uninstalls the given cask
- list: Lists installed casks
- outdated: List all outdated casks
- upgrade: Upgrades all outdated casks
You don’t have to remember the commands. If you ever forget a command, type in brew cask to see the list. You can also take a printout of the manual page and open it in the Preview app.
Mac Terminal Install Command
This syntax will export the man page output to Preview.
For example, the below string will open the manual page for brew cask in Preview:
Once the man page opens in the Preview app, choose File > Export As PDF to save the file as a PDF document for future reference.
Installing Mac Apps With Cask
You probably have a list of frequently used apps you install on every new Mac. Instead of doing so individually, you can install those apps through Cask. To search for an app, use this syntax:
Let’s see if there’s a Cask for Firefox. To do so, type this into Terminal:
As you might know, Firefox supports many different release channels. Mozilla uses these channels to slowly roll out updates to users, starting with daily Nightly builds to more Stable builds. If you want to install Nightly build of Firefox, you would type:
Or to install the Google Chrome Beta, try this:
Once you get relevant matches, enter:
Sometimes, you might not remember a particular app name. Thankfully, you just need to enter some relevant keywords and Cask will search for apps that contain them. The below screenshot shows what happens when you enter this command:
Uninstalling Apps With Cask
To uninstall Chrome Beta, simply type:
For uninstalling Firefox, use:
Mac Terminal Tutorial
The app gets uninstalls completely with no traces left behind. Once you install an app with Cask, it’s fine to update the app even if Cask doesn’t show updates. Don’t forget to check for configuration issues to further mitigate any problems. You can do so with this command:

Before checking for any Cask upgrade, don’t forget to periodically update the Homebrew core and casks. To do this, type:
GUI Versions of Homebrew and Casks
Although there is no GUI app to install Homebrew and Casks, there are third-party apps that lets you update Homebrew core, check configuration issues, install and update apps from Cask repository, and much more.
Cakebrew is a free, open source app that works in tandem with Homebrew. It lets you see the list of formulas you’ve installed, plus it can run a quick search and show the description of formulas you want to install. This is functionality the command line version doesn’t have.
If you like Homebrew, but don’t want to use the command line for every purpose, this app will prove useful to you. To install Cakebrew, type in:
Open Terminal In Mac
Homebrew and Cask Workflow for Alfred lets you easily install, uninstall, and manage Homebrew and casks in tandem. The script filters brew and cask with support for doctor, install, list, search, uninstall, and more.
Then launch Alfred, type in brew or cask, and you can manage your apps right there in Alfred. You need to have the Alfred Powerpack installed to use this and other workflows.
Install These Open Source Mac Apps
Mac Install Software From Unidentified Developer Terminal
Homebrew is a great package manager to install free Unix tools and macOS apps. If you’re setting up a Mac from scratch or work in a company where you manage multiple Macs, Homebrew can save you a lot of time and energy.
It’s easy to get lost with all these commands, but you don’t have to hurry. Go slow with these steps and take notes frequently. You might also bookmark this guide to Mac Terminal for other commands and help down the road, as well as some tips for customizing Terminal How to Customize the Mac Terminal and Make It More UsefulThe Terminal app on your Mac is powerful, but it's a bit bland out of the box. Here's how to personalize Terminal for your needs. Read More .
Mac Install App From Terminal
Although you might want to install common Mac apps at first, take a look at some lesser-known open source Mac apps 15 Free Open-Source Mac Apps You Must InstallWant to use some open source software on your Mac? These macOS apps are open-source, awesome, and best of all... free! Read More and install them with Homebrew Cask too.